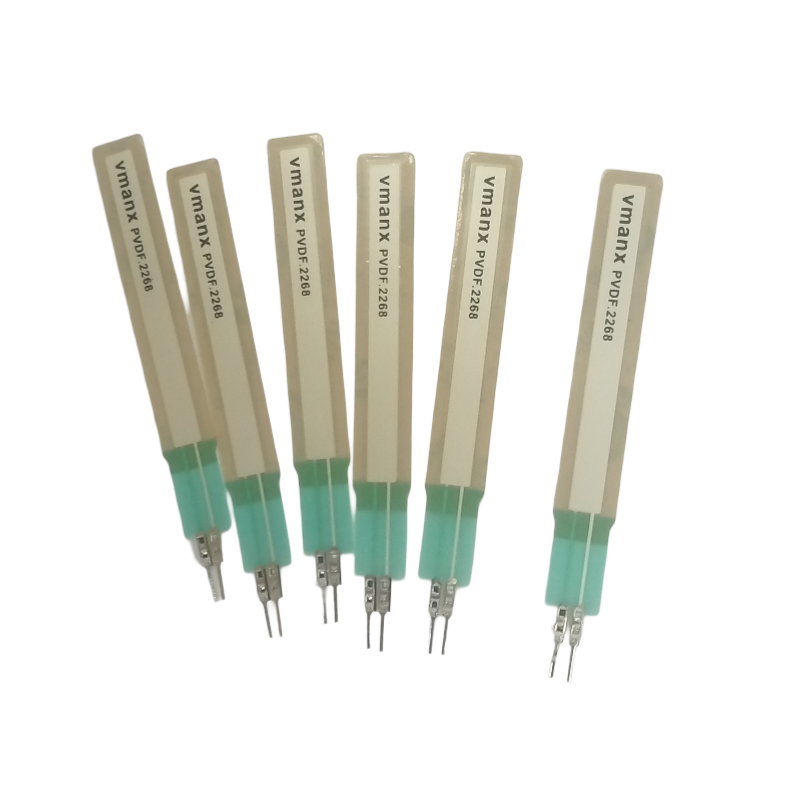

Medical field,Aerospace industry,Industrial applications,Environmental monitoring,Structural health monitoring ,etc..
Product Specification:
Piezoelectric pressure sensor PVDF-2268
1. Medical field: PVDF sensors are used in medical devices for applications such as monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs.
2. Aerospace industry: PVDF sensors are used in aircraft and spacecraft for measuring pressure, temperature, and vibration.
3. Industrial applications: PVDF sensors are used in industrial processes for monitoring levels, flow rates, and detecting leaks in pipelines.
4. Environmental monitoring: PVDF sensors are used in environmental monitoring systems for measuring pollution levels, air quality, and water quality.
5. Structural health monitoring: PVDF sensors are used in structural health monitoring systems to detect cracks, deformation, and other structural changes in buildings and bridges.
Overall, PVDF sensors are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications where accurate and reliable sensing is required.
Features :
- High sensitivity and accuracy
- Wide operating temperature range
- Fast response time
- Compact size for easy installation
- Versatile mounting options
- Reliable performance in various environments
Piezoelectric Thin Film Sensor Technical Manual :
As an actuator, polymers' low acoustic impedance allows them to be effectively used to deliver energy to air and other gases.
Table 1. Typical characteristic parameters of piezoelectric films
|
Symbol |
Parameter |
PVDF |
Interpolymer |
Unit |
|
T |
Thickness |
44-220 |
Various |
um(micron,10-6) |
|
d31 |
Piezoelectric strain constant |
23 |
11 |
|
|
d33 |
|
-25 |
-30 |
|
|
g31 |
Piezoelectric stress constant |
216 |
162 |
|
|
g33 |
|
-330 |
-542 |
|
|
k31 |
Electromechanical coupling constant |
12% |
20% |
|
|
Kt |
|
14% |
25-29% |
|
|
C |
Capacitance |
380(28μm) |
68(100μm) |
PF/cm2@1kHz |
|
Y |
Young’s modulus |
2-4 |
3-5 |
109N/m2 |
|
V0 |
Speed of sound tensile thickness |
1.5 2.2 |
2.3 2.4 |
103m/s2 |
|
P |
Thermoelectric coefficient |
30 |
40 |
10-6C/m20K |
|
E |
Dielectric constant |
106-113 |
65-75 |
10-12F/m |
|
ε/ε0 |
Relative dielectric constant |
12-13 |
7-8 |
|
|
ρn |
Mass density |
1.78 |
1.82 |
103kg/m |
|
ρe |
Volume resistivity |
>1013 |
>1014 |
Resistance meter |
|
R R |
Surface metallization resistivity |
2.0 |
2.0 |
Ω/square(CuNi) |
|
|
|
0.1 |
0.1 |
Ω/square(Ag ink) |
|
tan |
Loss tangent |
0.02 |
0.015 |
@1kHz |
|
|
Yield strength |
45-55 |
20.30 |
106N/M2(tensile axis) |
|
|
Temperature range |
-40-80 |
-40 to 115...145 |
℃ |
|
|
Water absorbency |
<0.02 |
<0.02 |
%H2O |
|
|
Maximum working voltage |
750(30) |
750(30) |
V/mil(V/μm),DC,@25℃ |
|
|
Breakdown voltage |
2000(80) |
2000(80) |
V/mil(V/μm),DC,@25℃ |
Table 2 Comparison table of piezoelectric materials
|
Characteristic |
Unit |
PVDF thin film |
PZT |
BaTiO3 |
|
Density |
103kg/m3 |
1.78 |
7.5 |
5.7 |
|
Relative dielectric constant |
ε/ε0 |
12 |
1.200 |
1.700 |
|
d31 constant |
(10-12)C/N |
23 |
110 |
78 |
|
g31 constant |
(10-3)Vm/N |
216 |
10 |
5 |
|
k31 constant |
% at 1kHz |
12 |
30 |
21 |
|
Acoustic impedance |
(106)kg/m2-sec |
2.7 |
30 |
30 |